






Globally, India leads in rice cultivation area and ranks second in production after China, contributing 21.5% to global production. Nationally, rice covers 25% of cultivated land and makes up 40-43% of total foodgrain production. However, common white rice lacks essential vitamins and minerals, leading to health issues.
Fortification involves adding nutrients like iron, folic acid, and vitamin A directly to rice, addressing deficiencies. This process creates fortified rice by dusting with a nutrient mix or mixing coated fortified kernels with non-fortified rice in ratios of 0.5%–2%, improving its nutritional value.
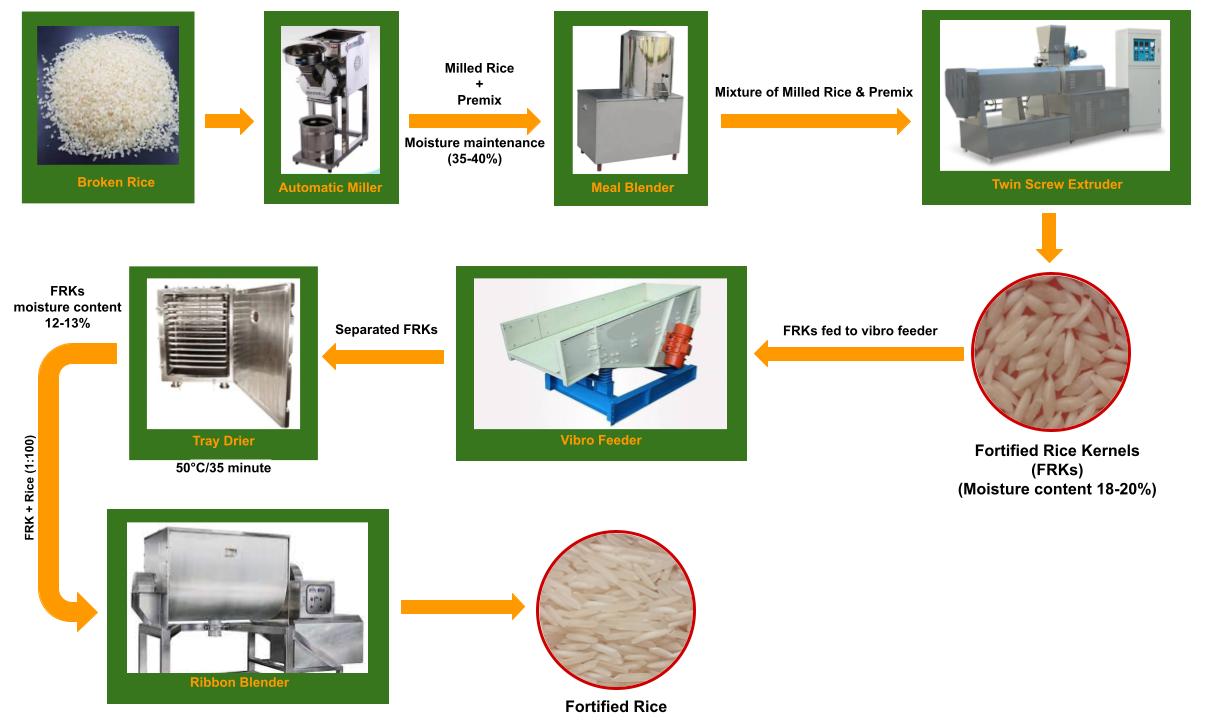
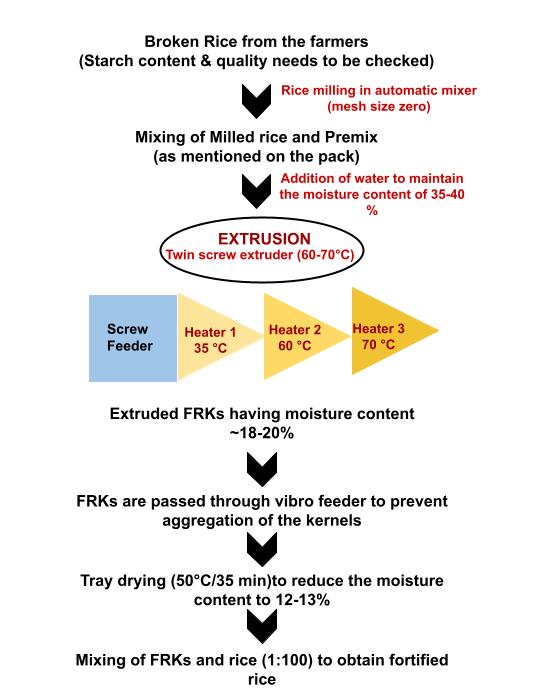
Fortified Rice Kernels (FRK) are rice grains shaped and enriched with vital vitamins and minerals to boost their nutritional value. This fortification process includes extruding a blend of milled rice and a premix containing essential nutrients or coating whole rice kernels with these vital elements. The resultant FRK can be effortlessly mixed with conventional rice, providing a convenient and efficient means to enhance the nutritional profile of this dietary staple.

Details about premix composition and extrusion/dusting technologies: the premix comprises micronized ferric pyrophosphate or Sodium Iron (III) EDTA, folic acid, cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin, plus other compounds like Zinc Oxide (ZnO), Retinyl Palmitate, Thiamine Hydrochloride, etc. This is then blended with polished rice at about a ratio of 1:100. :contentReference[oaicite:6]{index=6}
Technologies used: Coating, Dusting, Extrusion. In India, extrusion technology is commonly used to create rice-like fortified kernels which resemble normal rice and can be blended at ratios of approximately 1:50 to 1:200.
Micronutrient-rich rice enriched with iron, folic acid and vitamins; anemia prevention; cognitive boost; public health impact; accessible solution – widely consumed, no change in dietary habits needed.
The Innovation Hub for Rice Fortification (IHRF) is an innovative partnership that brings together collaborators such as Food Industry Resource Centre of India (FICSI), IIT Delhi, IIT Kharagpur, NIFTEM-K and Central Food Technological Research Institute (CFTRI) Mysore.